- Given a binary tree in java, traverse the binary tree using non recursive algorithm.
- Binary Tree traversal is categorized into two parts.
- Depth First Search (DFS) Traversal
- Pre Order Traversal
- Post Order Traversal
- In Order Traversal
- Breadth First search (BFS) or Level Order Traversal.
- In breadth first search algorithm, we are traversing the binary tree breadth wise (instead of depth wise).
- Depth First Search (DFS) Traversal
Examples of breadth first search algorithm.
Example 1:
Traverse the binary tree using level order traversal or BFS algorithm
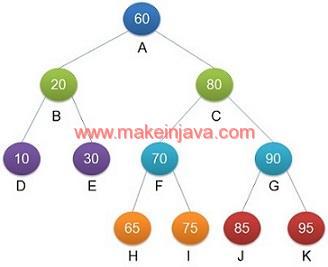
In level order traversal, we will traverse the binary tree level by level (or breadth wise) and algorithm is as follows:
- Go to level 0 & visit all nodes
- Visit Node A(100)
- Go to next level i.e. level 1 & visits all nodes
- Visit nodes Node B and Node C
- Go to level 2 & visits all nodes
- Visit nodes Node D, Node E, Node F & Node G
- Go to level 3 & visits all nodes
- Visit nodes Node H, Node I, Node J & Node K
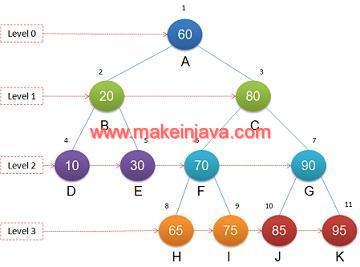
Algorithm: Breadth first search tree traversal
- Create a queue and push root node in queue.
- Iterate through the Queue (till queue is empty)
- Pop node from queue & prints its value.
- Insert left & right child to queue
- Loop finished
- We have visited & printed all nodes of a binary tree
- Output will be: 60 20 80 10 30 70 90 65 75 85 95
- We have visited & printed all nodes of a binary tree
- We have visited binary tree (level by level)
- Level 0 -> Level 1 -> Level 2 -> Level 3.
Time complexity of algorithm is O(n).
Program- Level order binary tree traversal in java
1.) TreeTraversalBFS Class:
- TreeTraversalBFS class is responsible for traversing the binary tree using breadth first search or level order traversal.
package org.learn.Question;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.Queue;public class TreeTraversalBFS { public static void traverseBinaryTree(Node root) { if (root == null) { System.out.println("Tree is empty"); return; } Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node node = queue.poll(); System.out.printf("%d ", node.data); if (node.left != null) { queue.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null) { queue.offer(node.right); } } }} |
2.) Node Class:
- Node class is representing the nodes of a binary tree.
package org.learn.Question;public class Node { public int data; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int num) { this.data = num; this.left = null; this.right = null; } public Node() { this.left = null; this.right = null; } public static Node createNode(int number) { return new Node(number); }} |
3.) App Class:
- We are constructing the binary tree in main method
- We will invoke method of TreeTraversalBFS class, to print the binary tree using BFS algorithm.
package org.learn.Client;import org.learn.Question.Node;import org.learn.Question.TreeTraversalBFS;public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { // root level 0 Node A = Node.createNode(60); // Level 1 Node B = Node.createNode(20); Node C = Node.createNode(80); // Level 2 Node D = Node.createNode(10); Node E = Node.createNode(30); Node F = Node.createNode(70); Node G = Node.createNode(90); // Level 3 Node H = Node.createNode(65); Node I = Node.createNode(75); Node J = Node.createNode(85); Node K = Node.createNode(95); // connect Level 0 and 1 A.left = B; A.right = C; // connect level 1 and level 2 B.left = D; B.right = E; C.left = F; C.right = G; // connect level 2 and level 3 F.left = H; F.right = I; G.left = J; G.right = K; System.out.println("Level order traversal or BFS of binary tree:"); TreeTraversalBFS.traverseBinaryTree(A); }} |
Output: binary tree traversal – breadth first search
Level order traversal or BFS of binary tree:60 20 80 10 30 70 90 65 75 85 95 |
Code – binary tree traversal level order traversal (BFS)
