- Given a binary tree, find out the height of binary using non recursive algorithm.
- Traverse the binary tree using level order traversal or breadth first search algorithm.
- What is height of Binary tree?
- The longest path from root to deepest leaf node, defines the height of a binary tree.
- Root node of a binary tree is assumed to be at Height 1.
- Calculate the height of binary tree wrt. root node.
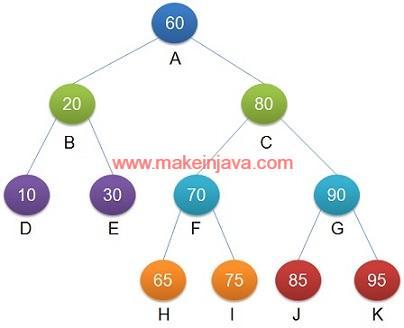
Example: find height of a binary tree in java using non recursive algorithm.
- Root Node 60 is at Height 1
- Nodes 20, 80 are at Height 2
- Nodes 10,30,70,90 are at Height 3
- Nodes 65,75,85,95 are at Height 4
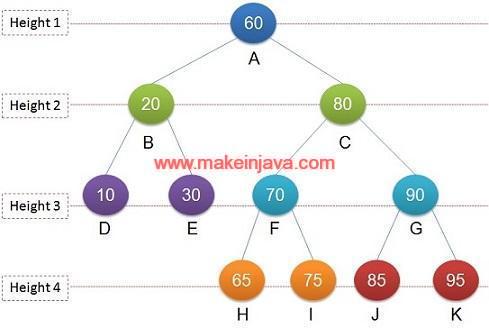
Longest path from Root to deepest node is at Height 4.
Algorithm: calculate height of binary tree using breadth first search
- Root is at height 1.
- Push root node to queue.
- Add null to the queue
- null will be level delimiter (marker that we have finished the current level)
- Start iterating through the Queue till it is empty
- Pop node from queue
- Check node is null (if yes, we are next level)
- Increment height by 1 & add level delimiter (null)
- Add next level children (left or/and right)
- At end of iteration, we will get the height of tree
Time complexity of algorithm is O(n).
Program: find height of binary tree in java using non recursive algorithm
1.) HeightOfTree Class:
- HeightOfTree class is responsible for finding the height of a binary tree.
- We will traverse the binary tree using level order traversal or non recursive algorithm.
package org.learn.Question;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class HeightOfTree {
public static int heightOfTree(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
System.out.println("Tree is empty");
return -1;
}
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>();
queue.offer(root);
// level delimiter
queue.offer(null);
int height = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node node = queue.poll();
if (null == node) {
if (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// level delimiter
queue.offer(null);
}
height++;
} else {
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return height;
}
}
2.) Node Class:
- Node class is representing the node(s) of a binary tree.
package org.learn.Question;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int num) {
this.data = num;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
public Node() {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
public static Node createNode(int number) {
return new Node(number);
}
}
3.) App Class:
- We are constructing the binary in main method.
- We are calling method of HeightOfTree class to find height of binary tree using BFS or level order traversal algorithm.
package org.learn.Client;
import org.learn.Question.HeightOfTree;
import org.learn.Question.Node;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// root level 0
Node A = Node.createNode(60);
// Level 1
Node B = Node.createNode(20);
Node C = Node.createNode(80);
// Level 2
Node D = Node.createNode(10);
Node E = Node.createNode(30);
Node F = Node.createNode(70);
Node G = Node.createNode(90);
// Level 3
Node H = Node.createNode(65);
Node I = Node.createNode(75);
Node J = Node.createNode(85);
Node K = Node.createNode(95);
// connect Level 0 and 1
A.left = B;
A.right = C;
// connect level 1 and level 2
B.left = D;
B.right = E;
C.left = F;
C.right = G;
// connect level 2 and level 3
F.left = H;
F.right = I;
G.left = J;
G.right = K;
int height = HeightOfTree.heightOfTree(null);
if (height > 0) {
System.out.println("Height of a Binary Tree : " + height);
} else {
System.out.println("Unable to calculate height of a binary tree");
}
}
}
Output: Height of binary tree using breadth first search algorithm
Height of Binary Tree : 4
