- Given a binary tree, We would like to find out, whether leaf nodes of a binary are at same level.
- We will use level order traversal or breadth first search (BFS) algorithm to traverse the binary tree.
- What is level in a binary tree?
- Level is distance or hops of node with respect to root node.
- The root node is considered to be at level 0 and immediate children of root node will be at level 1 (level of root node + 1).
- We can calculate the level of all the nodes in binary tree (Refer Fig 1).

Example 1: Given a binary tree (Fig 2), Check whether leaf nodes are at same level.
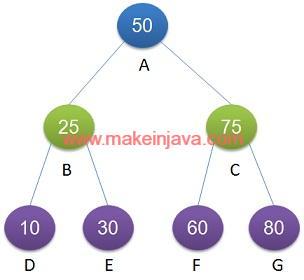
- Traverse the binary tree using breadth first search algorithm.
- Find out the level of each leaf node. (refer below table).
| S. No. | Leaf Node | Level |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | D | 2 |
| 2 | E | 2 |
| 3 | F | 2 |
| 4 | G | 2 |
- Create variable level=0, signify the level of binary tree
- Root is at level 0, push the root to queue.
- Add null to the queue (delimiter to know that we have finished the current level)
- Iterate through the Queue
- Pop node from queue
- Check node is null [The delimiter added earlier]
- We are at next level and increment the level
- Verify that popped up node is leaf node (or not)
- First time, we are visiting the leaf node
- Note down the level of leaf node and mark it visited.
- We got the leaf node again
- Compare the already stored level with current level
- If difference return false
- Compare the already stored level with current level
- Else perform rest operations
- First time, we are visiting the leaf node
- Add next level children (left & right child)
- Once we exit the loop, we will know, whether leaves are same level (or not)
Example 2: Check level of leaf nodes in a given binary tree (Fig 3)
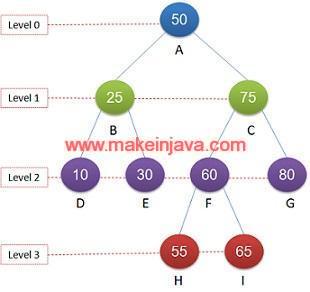
We will follow the similar algorithm for current example and we will find out level of each leaf node.
Time complexity: O(n).
Let us look into the complete code as follows:
1.) IsLeafAtSameLevel Class: IsLeafAtSameLevel class is used to check whether leaf nodes of binary tree are at same level using breadth first search recursive algorithm.
package org.learn.Question;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.Queue;public class IsLeavesAtSameLevel { public static boolean isLeavesAtSameLevel(Node root) { if (root == null) { System.out.println("Tree is empty"); return false; } Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); queue.offer(root); // level delimiter queue.offer(null); int level = 0; boolean bLeafFound = false; int leafLevel = -1; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node node = queue.poll(); // Level change if (null == node) { if (!queue.isEmpty()) { // level delimiter queue.offer(null); } level++; } else { if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { // first leaf found if (bLeafFound == false) { bLeafFound = true; leafLevel = level; } else { // Leaves are at different level if (leafLevel != level) { return false; } } } if (node.left != null) { queue.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null) { queue.offer(node.right); } } } return true; }} |
2.) Node Class: Node class representing the nodes of a binary tree. Node class has following attributes
- Data Node
- left child
- right child
package org.learn.Question;public class Node { public int data; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int num) { this.data = num; this.left = null; this.right = null; } public Node() { this.left = null; this.right = null; } public static Node createNode(int number) { return new Node(number); }} |
3.) App Class : We are creating the binary tree in main function & we are calling IsLeafAtSameLevel class, to find out whether leaf nodes are at same level using level order traversal.
package org.learn.Client;import org.learn.Question.IsLeavesAtSameLevel;import org.learn.Question.Node;public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) { //root level 0 Node A = Node.createNode(50); //Level 1 Node B = Node.createNode(25); Node C = Node.createNode(75); //Level 2 Node D = Node.createNode(10); Node E = Node.createNode(30); Node F = Node.createNode(60); Node G = Node.createNode(80); //Level 3 Node H = Node.createNode(55); Node I = Node.createNode(65); //connect Level 0 and 1 A.left = B; A.right = C; //connect level 1 and level 2 B.left = D; B.right = E; C.left = F; C.right = G; boolean isLeafAtSameLevel = IsLeavesAtSameLevel.isLeavesAtSameLevel(A); if(isLeafAtSameLevel) { System.out.println("1. Leaf nodes of binary tree are at same level"); } else { System.out.println("1. Leaf nodes of binary tree are not at same level"); } //Connect level 2 and level 3 F.left = H; F.right = I; isLeafAtSameLevel = IsLeavesAtSameLevel.isLeavesAtSameLevel(A); if(isLeafAtSameLevel) { System.out.println("2. Leaf nodes of binary tree are at same level"); } else { System.out.println("2. Leaf nodes of binary tree are not at same level"); } }} |
The output of main function [Fig 2 and Fig 3] is as follows:
1. Leaf nodes of binary tree are at same level2. Leaf nodes of binary tree are not at same level |
Download Code – Level of leaf node in binary tree (BFS)
