What is LinkedList Collection in Java?
- Linked list collection is a doubly-linked list.
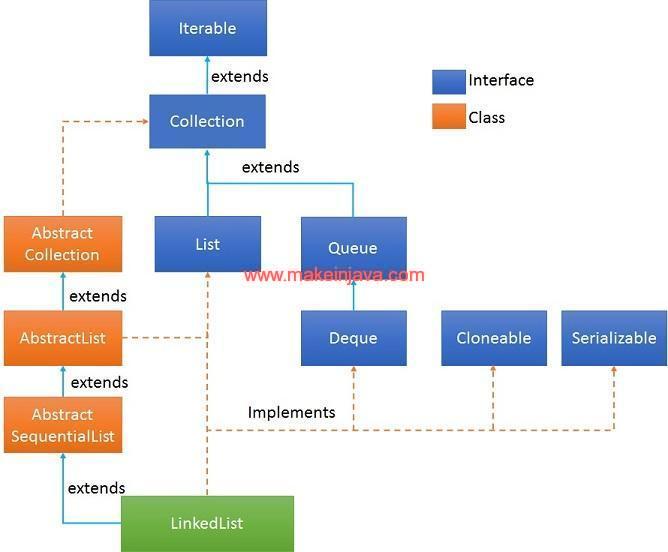
- LinkedList extends AbstractSequentialList class & implements List, Deque, Cloneable, Serializable interfaces.
- Insertion order is maintained in a linked list.
- LinkedList class is not thread safe.
- In multi threaded environment, it should be synchronized externally.
- The iterators returned by LinkedList class’s iterator and listIterator methods are fail-fast.
- LinkedList class can contain duplicate elements.
2. Class hierarchy of LinkedList:
3. Add or insert methods of LinkedList in java (with example):
| No. | Method Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | boolean add(E e) | Appends the specified element to the end of this list. |
| 2 | void add(int index, E element) | Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list. |
| 3 | boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) | Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified collection's iterator. |
| 4 | boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) | Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this list, starting at the specified position. |
| 5 | void addFirst(E e) | Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list. |
| 6 | void addLast(E e) | Appends the specified element to the end of this list. |
4. Program – Add or insert nodes to linkedlist in java (example)
package org.learn.collection.list.linkedlist;import java.util.LinkedList;public class DemoAddToLinkedList { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>(); linkedList.add("canoe"); System.out.println("Demo of add methods of LinkedList class: "); demoAddMethod(linkedList); } private static void demoAddMethod(LinkedList<String> linkedList) { // [canoe] System.out.println("1. Orignal LinkedList:" + linkedList); linkedList.add(0, "archery"); linkedList.add(2, "canoe"); // [archery, canoe, canoe] System.out.println("2. Added element at 0 and 2 index: " + linkedList); linkedList.add("diving"); // [archery, canoe, canoe, diving] System.out.println("3. Added element in list: " + linkedList); LinkedList<String> addElementsList = new LinkedList<>(); addElementsList.add("squash"); addElementsList.add("bowling"); // It will add elements to last of list linkedList.addAll(addElementsList); // [archery, canoe, canoe, diving, squash, bowling] System.out.println("4. Added another list : " + linkedList); LinkedList<String> anotherList = new LinkedList<>(); anotherList.add("golf"); anotherList.add("judo"); // It will add elements from index 1 linkedList.addAll(1, anotherList); // [archery, golf, judo, canoe, canoe, diving, squash, bowling] System.out.println("5. Added another list at index 1 : " + linkedList); // It will add element before head i.e. first element of list of list linkedList.addFirst("squash"); // [squash, archery, golf, judo, canoe, canoe, diving, squash, bowling] System.out.println("6. Added element before head : " + linkedList); // It will add elements to last of list linkedList.addLast("judo"); // [squash, archery, golf, judo, canoe, canoe, diving, squash, bowling, judo] System.out.println("7. Added element to after tail node : " + linkedList); }} |
5. Output – Add or insert elements/ nodes to linkedlist in java
Demo of add methods of LinkedList class: 1. Orignal LinkedList:[canoe]2. Added element at 0 and 2 index: [archery, canoe, canoe]3. Added element in list: [archery, canoe, canoe, diving]4. Added another list : [archery, canoe, canoe, diving, squash, bowling]5. Added another list at index 1 : [archery, golf, judo, canoe, canoe, diving, squash, bowling]6. Added element before head : [squash, archery, golf, judo, canoe, canoe, diving, squash, bowling]7. Added element to after tail node : [squash, archery, golf, judo, canoe, canoe, diving, squash, bowling, judo] |
